CyFi-TTS [ICASSP 2023]
in Seminar on Text-to-Speech
Cyclic Normalizing Flow with Fine-Grained Representation for End-to-End Text-to-Speech
LG Uplus Corp. (황인선, 한용섭, 전병기)
Abstract
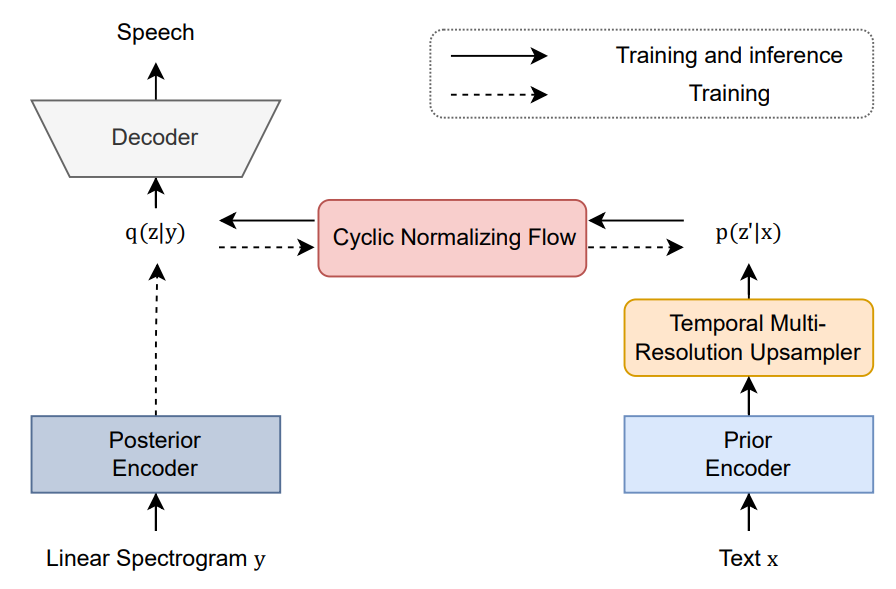
- End-to-End 기반의 TTS는 학습 때 사용된 seen dataset에 대해서는 좋은 성능을 보이지만, unseen transcript에 대해서 inference하는 것에는 어려움이 존재함
- 텍스트와 스피치 사이의 information gap을 만드는 one-to-many 문제를 해결하기 위해 cyclic normalizing flow를 제안하고자 함
- Temporal multi-resolution upsampler (TMRU), Cyclic normalizing flow (CNF) 도입
- VITS [J. Kim et al., 2021] 기반 모델
- 실험결과: MOS 4.02, CER 1.99%
Goal
- fine-grained representation을 갖는 cyclic normalizing flow를 제안하여 information gap을 해결하고 natural-sounding speech를 생성해내고자 함
Motivation
- 기존의 TTS 시스템은 unseen transcript로 inference하면 mispronunciation된 스피치를 생성하는 문제가 존재함
- 텍스트와 스피치의 정보 차이 때문에 확장된 언어적 representation과 acoustic representation을 매칭하는 것이 쉽지 않음
Methods
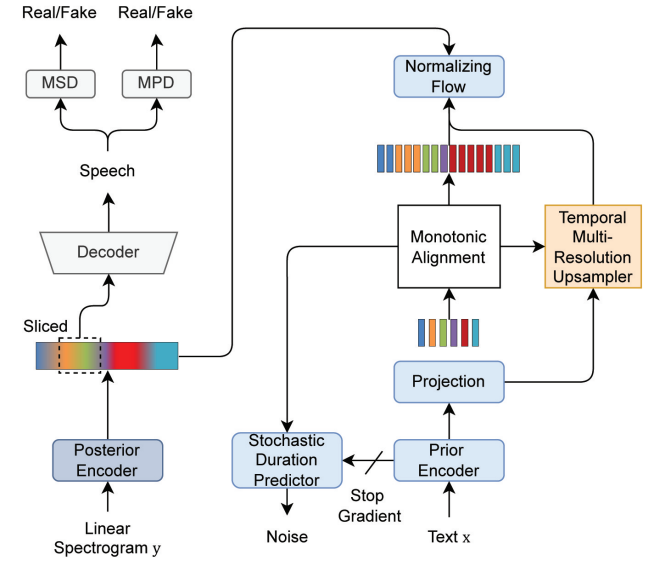
1. Prior and Posterior Encoder
- Prior encoder: text에 포함되어있는 linguistic representation을 추출함 (=coarse-grained)
- MAS: 텍스트와 스피치 간의 alignment를 추정함
- alignment을 사용하여 coarse-grained linguistic representation을 acoustic representation으로 확장함
- Posterior encoder: 주어진 speech로부터 acoustic representation을 추출함
- information gap줄이기 위해 사용, but 시퀀스 확장할 때 information gap 발생
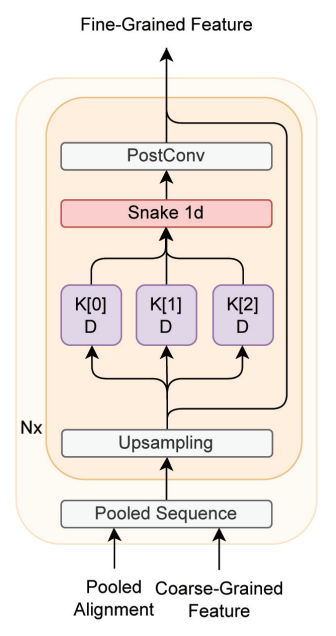
2. Temporal Multi-Resolution Upsampler (TMRU)
- information gap을 해결할 수 있는 fine-grained representation을 생성하고자 제안함
- Upsampler가 점진적으로 시퀀스를 확장하고 여러 프레임에 걸쳐 분포되어있는 expression들을 찾아냄으로써 빨라지거나 멈추는 문제를 완화함
- corase-grained representation $z_c \in \mathbb{R}^{L\times H}$ $\longrightarrow$ pooled representation $z_{c’} \in \mathbb{R}^{\frac{1}{2}T\times H}$
- L: phoneme 길이, H: feature dimension
- 다양한 커널 사이즈와 dilation을 가진 convolution을 사용하여 signal의 다양한 부분을 측정한 후, convolution의 합으로 signal의 주기적 요소를 추출함
- linguistic representation이 여러 frame에 걸쳐있기 때문
- kernel $K=[3, 5, 7]$, dilation $D=[1, 3, 5]$
- Snake function를 사용하여 다양한 expression을 탐색하기 위해 inductive bias를 적용함
- $f(x)=x+\frac{1}{\alpha}sin^2(\alpha x)$
- monotonicity + easy optimization
- 파라미터($\alpha$)를 통해 signal의 주기적 요소의 frequency를 컨트롤할 수 있음
- PostConv: temporal signal을 추출함
- 따라서 TMRU는 각 프레임마다 디테일한 정보를 제공하기 위해 temporal signal을 고려함으로써 fine-grained representation을 점진적으로 생성할 수 있음
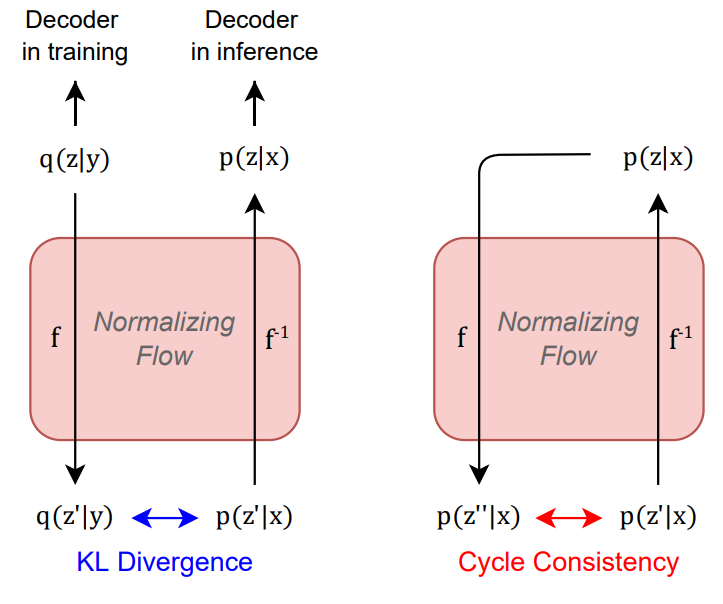
3. Cyclic Normalizing Flow (CNF)
- speech로부터 얻은 latent representation $q(z|y) \longrightarrow flow \longrightarrow q(z’|y)$
- text로부터 얻은 representation $p(z’|x) \longrightarrow flow^{-1} \longrightarrow p(z|x)$
- $q(z’|y)$와 $p(z’|x)$의 차이를 줄이기 위해 KL loss 사용
- $\mathcal{L}_{KL}=KL[q(z’|y)||p(z’|x)]$
- 학습 때는 디코더가 $q(z|y)$를 인풋으로 하지만, 인퍼런스 때는 $p(z|x)$를 인풋으로 하기 때문에 불일치 문제 발생함
- CNF를 통해 이를 해결하고자 함
- $\mathcal{L}_{cc}=KL[p(z’|x)||p(z’’|x)]$
- $p(z’|x) \longrightarrow p(z|x) \longrightarrow p(z’’|x) = f(f^{-1}(p(z’|x)))$
- $p(z’|x)$와 $p(z’’|x)$ 사이의 representation을 맞춰주고자함
4. Joint Training of the Acoustic Generator and Neural Vocoder
- Stochastic duration predictor, HiFi-GAN 사용
5. Training Objective Function
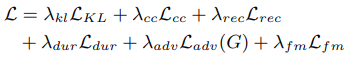
Experiments
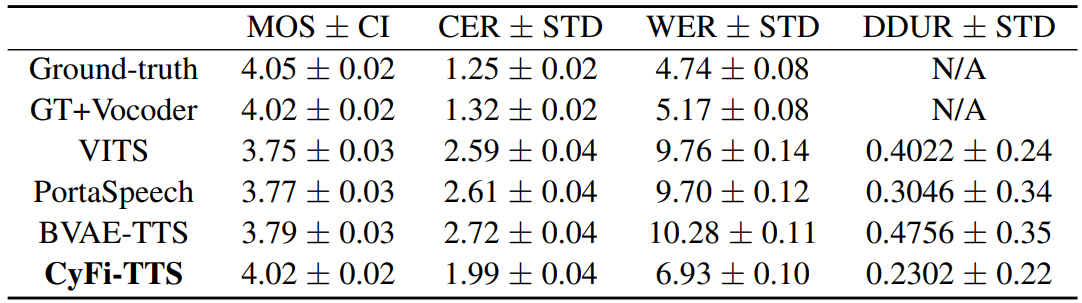
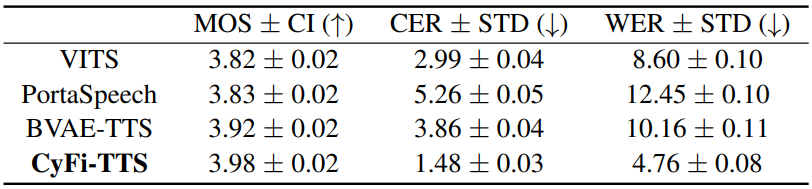
1. MOS
- seen dataset에 대해 4.02, unseen transcript에 대해 3.98
- 다른 비교모델보다 좋은 성능을 보임
2. CER, WER, DDUR
- CER (Character Error Rate)과 WER (word error rate)가 가장 낮은 수치를 보였고, 생성된 음성이 clear한 발음을 나타낸다는 것을 의미함
- DDUR (the average absolute duration difference)도 작은 값을 보였기 때문에, 생성된 발화와 target 발화의 길이가 유사하다는 것을 의미함
- 해당 모델이 upsampling 과정에서 디테일한 expression을 담아내기 때문에 텍스트와 프레임 간의 매핑 능력이 향상됨
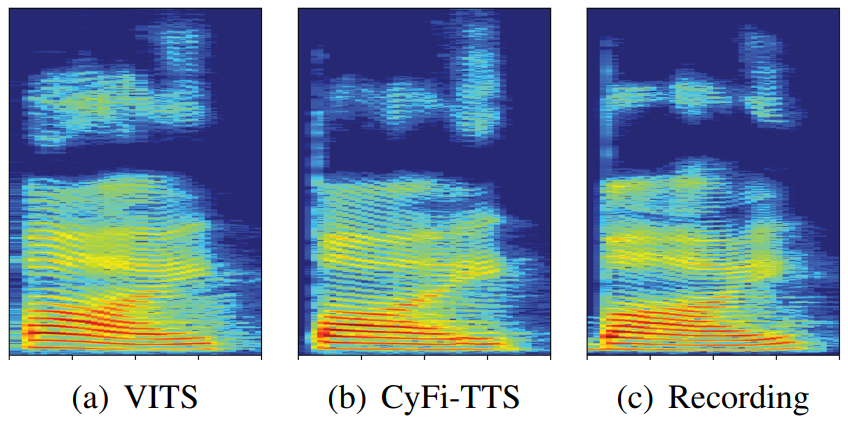
3. Ablation study
- spectrogram을 사용하여 생성된 스피치의 주파수 요소를 분석
- CyFi-TTS는 저주파수에서 GT와 비슷한 energy와 formant를 보임
- VITS가 CyFi-TTS보다 고주파수에서 목소리 특성이 덜 섬세하게 표현됨
$\Rightarrow$ CyFi-TTS가 VITS보다 고주파수와 저주파수 신호에서 fine-grained representation을 잘 표현함