Meta-StyleSpeech
in Seminar on Text-to-Speech
Goal
- 짧은 레퍼런스 오디오에도 높은 퀄리티로 Adaptation 할 수 있는 Multi-speaker TTS 모델
Motivation
- 짧은 Target Speech로부터 생성하는 Personalized Speech에 대한 수요 증가 → Multi-speaker TTS + Adapatation ability ****for unseen speaker 필요
- Adaptation 에 관한 이전 연구들
- 파인튜닝 방식 Sample Efficient Adaptive Text-to-Speech [Y. Chen et al., 2019] Neural Voice Cloning with a Few Samples [S. Arik et al., 2018] Adaspeech: Adaptive Text to Speech For Custom Voice [M. Chen et al., 2021] → ****파인튜닝에 시간이 많이 들고, Real-world scenario에 적용하기 어려움
- 레퍼런스 오디오에서 Latent vector 추출하는 방식 Towards End-to-End Prosody Transfer for Expressive Speech Synthesis with Tacotron [S. Ryan et al., 2018] Style Tokens: Unsupervised Style Modeling, Control and Transfer in End-to-End Speech Synthesis [Y. Wang et al., 2018] Transfer Learning from Speaker Verification to Multispeaker Text-to-Speech Synthesis [Y. Jia et al., 2018] → Source 데이터셋의 스피커 다양성에 의존하는 경향이 있어, Adaptation을 못할 때가 있고, 레퍼런스 오디오가 짧은 경우에 Adaptation 성능이 떨어짐
- 메타학습의 특징
- Few-shot 생성모델 관점에서 일반화 성능을 향상시킴
- 이미지 도메인에서 생성 및 분류 문제를 푸는데에 많은 연구가 진행되었음 → 성능과 효과는 좋지만 TTS에 직접적으로 적용한 선행 연구가 없음
Contribution
- 짧은 레퍼런스 오디오로부터 좋은 품질의 발화를 생성하는 Adaptive multi-speaker TTS 모델인 StyleSpeech를 제안
- 메타학습과 판별자를 추가로 적용하여 Unseen speaker에 대해서 Adaptation 성능을 높인 Meta-StyleSpeech 모델을 추가로 제안
- 기존의 Baseline 모델들을 뛰어넘고 SOTA 성능을 보임
Overview
빠른 흐름 파악을 위해 간소화하여 적어 놓았습니다. 자세한 설명은 아래에 있습니다.
StyleSpeech
레퍼런스 오디오 Mel을 Mel-스타일 인코더가 인코딩해서 스타일 정보를 Genertor한테 전달하고, Generator는 이 정보를 단순히 Concat해서 받는 것이 아니라 본 논문에서 새로 제안한 Style Adaptive Layer Normalization (SALN) 을 적용해서 스타일 정보를 받음. Generator의 기반모델은 FastSpeech2를 사용하였으며, Phoneme 인코더, Variance Apdator, Mel 디코더로 구성됨. 100,000 스텝동안 아래의 Reconstruction Loss를 줄이는 방식으로 Mel-스타일 인코더와 Generator를 학습함. \[\tilde{X}=G(t,w) \quad w=Enc_s(X) \\ \mathcal{L}_{recon} = \mathbb{E}[|| \tilde{X}-X||_1 ]\]
Meta-StyleSpeech
새로운 스피커의 짧은 레퍼런스 오디오에 대해 Adaptation 능력을 더 높이기 위해서, 메타학습 방식을 적용했음. 이 과정에서 쿼리 텍스트로 합성한 Mel $\tilde{X}_q$에 대해 오차를 비교할 GT-Mel이 존재하지 않음. 따라서 추가적으로 2개의 Discriminator(Style discriminator, Phoneme discriminator)를 함께 적용하여 적대적 신경망 구성으로 성능향상을 시키고자 함. 60,000 스텝동안 사전학습한 StyleSpeech를 이용해 40,000 스텝동안 아래의 Loss를 줄이는 방식으로 메타학습을 진행함. \[\mathcal{L}_{D_s} = \mathbb{E}_{t,w,s_i\sim S} [(D_s(X_s,s_i)-1)^2 + D_s(\tilde{X}_q, s_i)^2 ] \\ \mathcal{L}_{D_t} = \mathbb{E}_{t,w}[(D_t(X_s,t_s)-1)^2 +D_t(\tilde{X}_q,t_q)^2] \\ \mathcal{L}_{adv} = \mathbb{E}_{t,w,s_i\sim S}[(D_s(G(t_q,w_s),s_i)-1)^2] + \mathbb{E}_{t,w}[(D_t(G(t_q,w_s),t_q)-1)^2] \\ \mathcal{L}_{recon}=\mathbb{E}[||G(t_s,w_s)-X_s||_1] \\ \mathcal{L}_{G}=\alpha\mathcal{L}_{recon}+\mathcal{L}_{adv} \\ \\ \mathcal{L}_{D}=\mathcal{L}_{D_s}+\mathcal{L}_{D_t}+\mathcal{L}_{cls}\]
Architecture
StyleSpeech
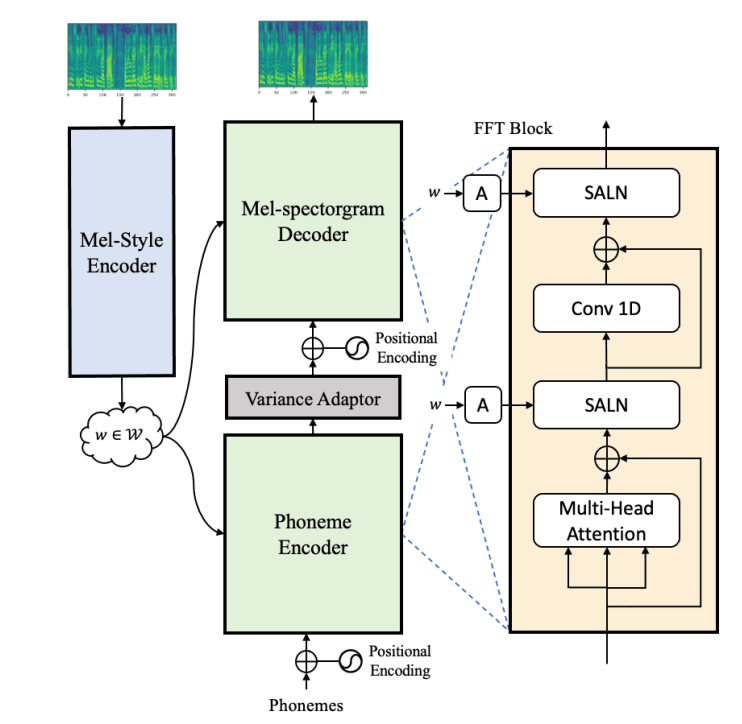
The architecture of StyleSpeech
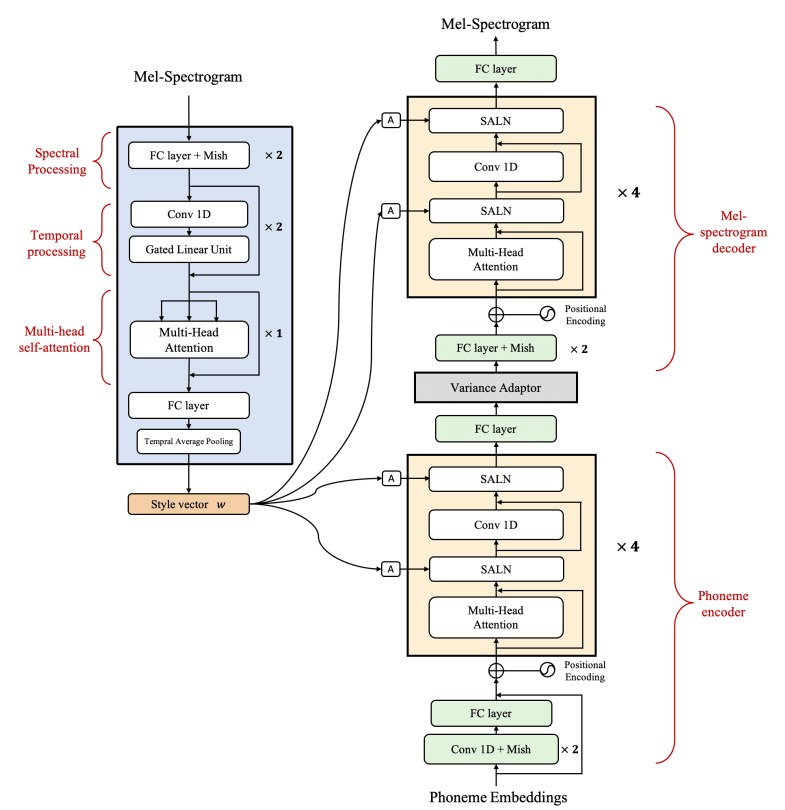
The detail architecture of StyleSpeech
Mel-style encoder (StyleSpeech)
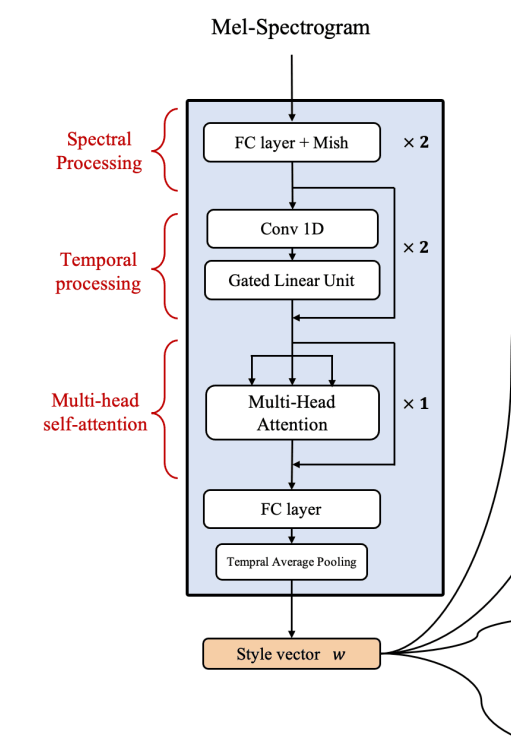
The architecture of Mel-style encoder
- 모델: $Enc_s(\cdot )$
- 인풋: Reference Speech $X$
- 아웃풋: Style vector $w\in \mathbb{R}^N$
- 스타일 벡터 $w$는 레퍼런스 스피치 $X$가 가지고 있는 스피커 정보와 프로소디 정보를 포함
- 기반 모델: Neural Voice Cloning with a Few Samples [S. Arik et al., 2018]
- [S. Arik, 2018] 에서 그랬듯이 Style encoder는 3가지 부분으로 나뉨
Spectral Processing (FC-layer)
Reference 오디오 Mel-스펙트로그램 각각의 프레임을 Hidden sequence로 변환
Temporal Processing (Gated CNN, Residual connection)
Sequential 정보를 Capture 함
Multi-head self-attention
Global 정보를 Encoding 함
[S. Arik, 2018] 에서는 오디오 샘플에 Multi-head self-attention을 적용했지만, 본 논문에서는 Frame-level 의 Multi-head self-attention을 적용 → 스타일 인코더가 짧은 Reference 오디오에 대해서도 스타일 정보를 잘 추출할 수 있게 함
Generator (StyleSpeech)
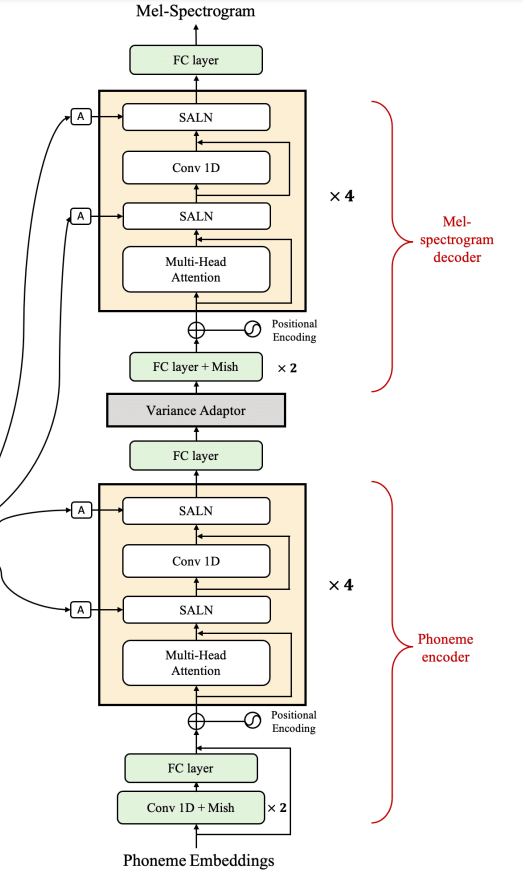
The architecture of generator
- 모델: $G$
- 인풋: Phoneme sequence $t$ , Style vector $w$
- 아웃풋: Target speech $\tilde{X}$
- 기반 모델: FastSpeech2: Fast and High-Quality End-to-End Text to Speech [Y. Ren et al., 2020]
- [Y. Ren, 2020] 에서 그랬듯이 Generator는 3가지 부분으로 나뉨
- Phoneme encoder
- Variance adpator
- Mel-spectrogram decoder
Style-adaptive layer norm (SALN)
\[\bold{y}= \frac{\bold{h}-\mu}{\sigma}, \quad \quad \mu= \frac{1}{H} \Sigma^H_{i=1} h_i, \quad \quad \sigma=\sqrt{\frac{1}{H} \Sigma^H_{i=1} (h_i-\mu)^2}\]where $\bold{h}=(h_1, h_2, …,h_H)$는 Given feature vector, $\bold{y}=(y_1, y_2, …,y_H)$ 는 Normalized vector \[SALN(\bold{h},w) = g(w)\cdot\bold{y}+b(w)\]
where $w$는 스타일 벡터 form 스타일 인코더, $g(\cdot),b(\cdot)$은 학습가능한 Gain과 Bias
- 배경: Generator 모델로 사용하는 FastSpeech2 [Y. Ren, 2020] 여러 목소리를 내지 못함. 그래서 보통 스타일 벡터를 Generator에게 전달함. 다른 연구들에서 일반적으로 스타일 벡터는 Generator의 인코더 아웃풋 혹은 디코더 인풋에 Concat 되거나, Summation 되는 형식으로 전달되어왔음. 또한 이를 대체하고자 SALN을 제안함
- 구성: $g(\cdot), b(\cdot)$ 각각 Single FC-layer
- 특징: Layer Normalization [L. Ba et al., 2016] 에서는 Gain과 Bias가 고정되었지만, 본 논문에서 제안한 SALN은 스타일 벡터 $w$에 기반하여 인풋 피쳐 벡터를 Adaptively하게 Scaling 하거나 Shifting 할 수 있음 ([L. Ba, 2016] 에서도 Gain과 Bias가 학습 가능한 파라미터였는데, 왜 고정됐다고 표현했는지 이해하지 못함)
- 기대 결과: SALN을 적용함으로써, 주어진 레퍼런스 오디오와 Phoneme 인풋에 대해 Generator는 Multi-speaker 스피치의 다양한 스타일을 합성할 수 있게 됨. (정규화된 데이터에 Scaling과 Shifting을 적용하는 것은 데이터의 분포를 유동성있게 변화시키는 것으로 이해할 수 있음)
Training (StyleSpeech)
\[\tilde{X}=G(t,w) \quad w=Enc_s(X)\] \[\mathcal{L}_{recon} = \mathbb{E}[|| \tilde{X}-X||_1 ]\]where $\tilde{X}$는 Generated Mel-spectrogram, $t$는 Input phoneme, $X$는 Ground truth Mel-spectrogram, $w$는 Style vector
- 학습 과정동안 Mel-style encoder에 다른사람의 스피치가 아닌 Ground truth Mel-spectrogram을 넣어줌
Meta-StyleSpeech
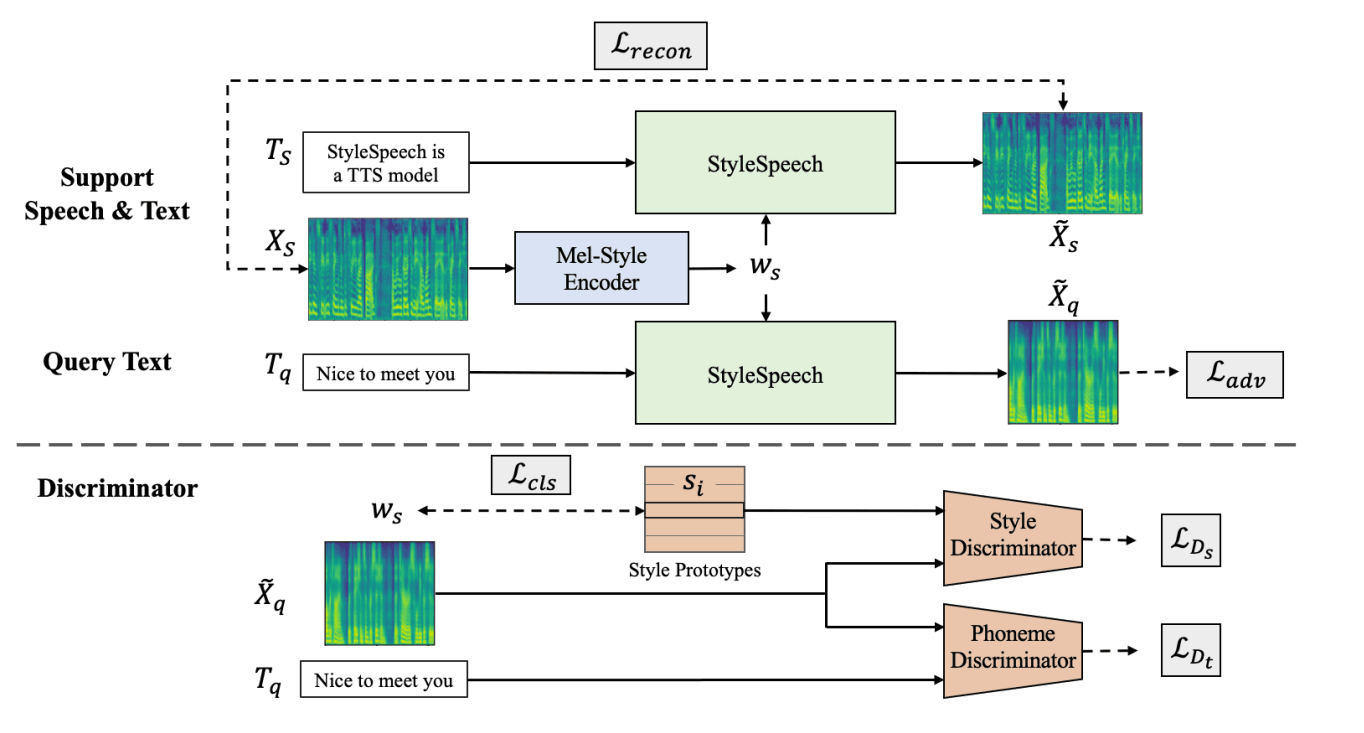
The overview of Meta-StyleSpeech
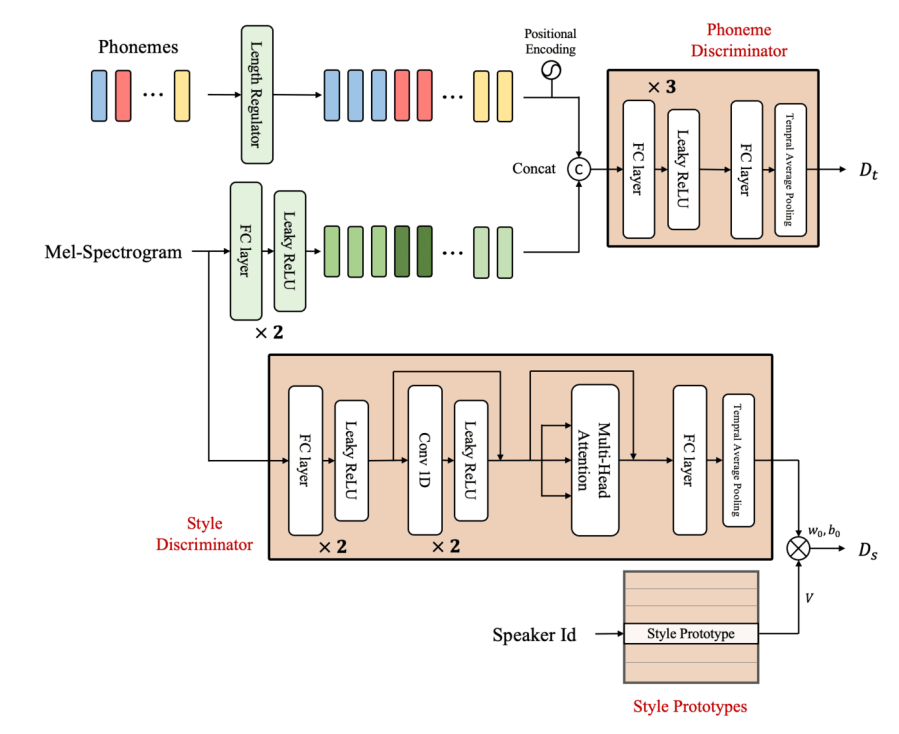
Architecure of Phoneme discriminator(up) and Style discriminator(down)
- 배경
- StyleSpeech가 SALN을 이용해서 Adaptation 성능을 높이고자 했지만, Unseen 스피커의 레퍼런스 오디오가 짧게 들어오면 완벽한 Adaptation을 하기에는 무리가 있음. 즉, Generalization 성능이 뛰어나지 않음
- 짧은 레퍼런스 오디오와 Unseen 스피커에 대한 Adaptation 성능을 높이기 위해 StyleSpeech 모델을 확장하고자 함
- Meta-learning 방식이 Few-shot learning에 Generalization 성능을 향상시켜줌
- 메타학습 방식을 이용해서 StyleSpeech를 확장하여 새로운 Meta-StyleSpeech를 제안
- Episodic 학습을 통해 Unseen 스피커에 대해서 One-shot learning을 Simulate 함
- Episode 마다 각각의 Target speaker $i$로 부터
- Support sample: 1개 (Speech, Text) 쌍 $(X_s,t_s)$
- Query sample: 1개 Text $t_q$
- Goal: Generate query speech $\tilde{X}_q$ (from query text $t_q$ and style vector $w_s$)
- 하지만 합성된 Query speech $\tilde{X}_q$ 와 비교할 Ground-truth Mel-spectrogram이 존재하지 X
- Discriminator를 추가로 사용해서 Adversarial 신경망 형태로 합성 성능을 높이자!
Style discriminator (Meta-StyleSpeech)
- 모델: $D_s (\cdot,\cdot)$
- 인풋: Mel-spectrogram and style vector $w_s$ of target speaker
- 아웃풋: Single scalar value (입력스피치 & 타겟 스타일 벡터가 동일한 화자에서 나왔을 판별 값)
Style prototype
- 모델: $S={s_i }^K_{i=1}$
- $K$ $K$
- $s_i\in \mathbb{R}^N$는 $K$명의 Speaker 중 $i$번째 $$Speaker에 대한 Style prototype
- 인풋: Style vector $w_s\in \mathbb{R}^N$ of target speaker
- 코드 상으로는 아래와 같이 초기값 선언
self.style_prototypes = nn.Embedding(n_speakers, style_dim)- n_speakers = $K$ 이고, style_dim = 128 (스타일 벡터 $w_s$의 dimension)
- 즉, $K$명의 스피커에 대해 Learnable한 128차원의 임베딩 값을 설정
- Training objective \(\mathcal{L}_{cls} = - \log \frac{\exp(w_s^\top s_i)}{\Sigma_{i^\prime}\exp(w_s^\top s_{i^\prime})}\) 스타일 벡터 $w_s$ 와 스타일 프로토타입 $s_i$ 간의 Dot product를 통해서 Style logit을 얻고, 이는 Cross entropy loss(Softmax 함수 포함)를 거쳐 스타일 프로토타입 $s_i$가 Target speaker의 공통의 스타일(speaker identity)를 표현할 수 있게끔 유도
Style discriminators
- 모델: $h(\cdot)$
- 인풋: Generated 스피치 $\tilde{X}_q$, 혹은 True 스피치 $X_s$
- 아웃풋: $M$-차원의 벡터
- 구성: Mel-style encoder와 굉장히 유사, Gated CNN → 1D CNN 으로 변경
- 모델: $S={s_i }^K_{i=1}$
- 최종 아웃풋 \(D_s(\tilde{X}_q,s_i) = w_0s_i^\top V\ h(\tilde{X}_q)+b_0\)
- $V\in \mathbb{R}^{N\times M}$은 그냥 Linear layer
- $w_0,b_0$는 학습 가능한 parameter
- 최종 Style discriminator loss function \(\mathcal{L}_{D_s} = \mathbb{E}_{t,w,s_i\sim S} [(D_s(X_s,s_i)-1)^2 + D_s(\tilde{X}_q, s_i)^2 ]\)
- Least Squares Generative Adversarial Networks [X. Mao et al., 2017] 을 참조
Phoneme discriminator (Meta-StyleSpeech)
- 모델: $D_t(\cdot,\cdot)$
- 인풋: Query speech $\tilde{X}_q$, Query text $t_q$ or Support speech $X_s$, Support text $t_s$
- 아웃풋: 입력 Speech가 True Speech인지를 판별한 확률 (Text를 condition으로 받음)
- 구성: FC-layer
- 특징
- 입력 Speech에 대해 Frame-level로 판별을 진행함
- 각 Phoneme마다 Duration을 알기 때문에, 각 프레임의 Mel-spectrogram을 그에 대응하는 Phoneme과 Concat하여 Discriminator를 통과함.
- Discriminator는 매 프레임마다 스칼라 값을 계산하고 평균내어서 1개의 스칼라 값을 얻음
- Phoneme discriminator loss function \(\mathcal{L}_{D_t} = \mathbb{E}_{t,w}[(D_t(X_s,t_s)-1)^2 +D_t(\tilde{X}_q,t_q)^2]\)
Generator (Meta-StyleSpeech)
- Query speech에 대한 Generator의 Adversarial loss function \(\mathcal{L}_{adv} = \mathbb{E}_{t,w,s_i\sim S}[(D_s(G(t_q,w_s),s_i)-1)^2] + \mathbb{E}_{t,w}[(D_t(G(t_q,w_s),t_q)-1)^2]\)
- Support speech에 대한 Generator의 Reconstruction loss function \(\mathcal{L}_{recon}=\mathbb{E}[||G(t_s,w_s)-X_s||_1]\)
Episodic meta-learning
전체적으로 본 논문에서는 아래와 같이 $\mathcal{L}{recon}$ 과 $\mathcal{L}{adv}$를 최소화하는 Generator와 $\mathcal{L}{D{s}}$, $\mathcal{L}{D{t}}$ 그리고 $\mathcal{L}{cls}$ 를 최소화하는 Discriminator를 번갈아가며 업데이트하는 방식으로 Meta-StyleSpeech를 메타학습을 진행 $$ \mathcal{L}{G}=\alpha\mathcal{L}{recon}+\mathcal{L}{adv}
\
\mathcal{L}{D}=\mathcal{L}{D_s}+\mathcal{L}{D_t}+\mathcal{L}{cls} $$ where $\alpha=10$
Experiment
- 데이터셋
- 학습용: LibriTTS (1141명, 110시간)
- Unseen speaker 평가용: VCTK (108명)
- Baselines
- GT : GT 스피치
- GT Mel : GT Mel + MelGAN 보코더
- DeepVoice3 : 멀티스피커 TTS 모델인데, look up table 사용해서 Seen 스피커에 대해서만 가능
- GMVAE : 멀티스피커 TTS 모델
- Multi-speaker FS2 : 멀티스피커 FastSpeech 2 모델인데, 스타일 벡터를 인코더 아웃풋과 디코더 인풋에 더해줌. 스타일 벡터는 멜-스타일 인코더에서 뽑음
- Multi-speaker FS2 + $d$-vector : 위에꺼랑 동일하지만, 스타일 벡터를 이미 학습된 Style verification 모델에서 뽑아옴([Wan et al., 2018] 에서 verification 모델 뽑아옴)
- StyleSpeech : 싱글 스피치 오디오로부터 멀티스피커 스피치를 만들어내는 모델
- Meta-StyleSpeech : 스타일 스피치 + 메타 학습
- 실험 결과
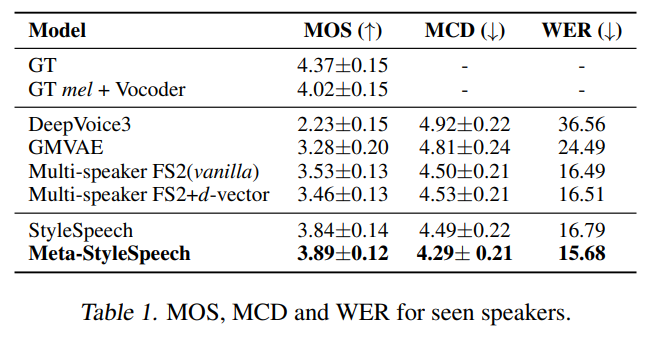
Table 1을 통해 Seen 스피커에 대한 합성 능력이 StyleSpeech와 Meta-StyleSpeech가 제일 좋다는 것을 알 수 있음.
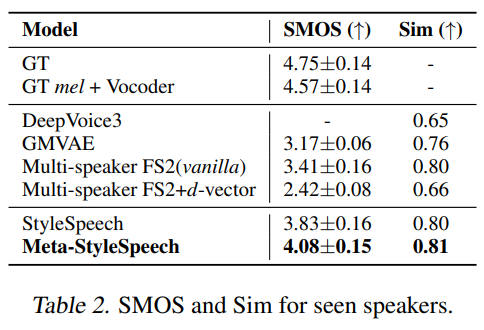
Table 2을 통해 타겟 목소리와의 유사도 또한 StyleSpeech와 Meta-StyleSpeech가 제일 좋다는 것을 알 수 있음.
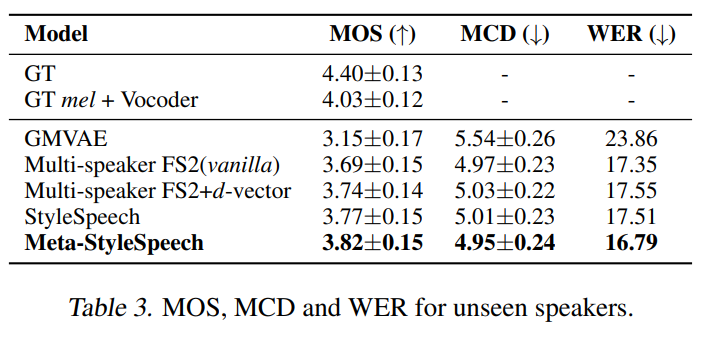
Table 3을 통해 Unseen 스피커에 대한 합성 능력이 Meta-StyleSpeech가 제일 좋다는 것을 알 수 있음.
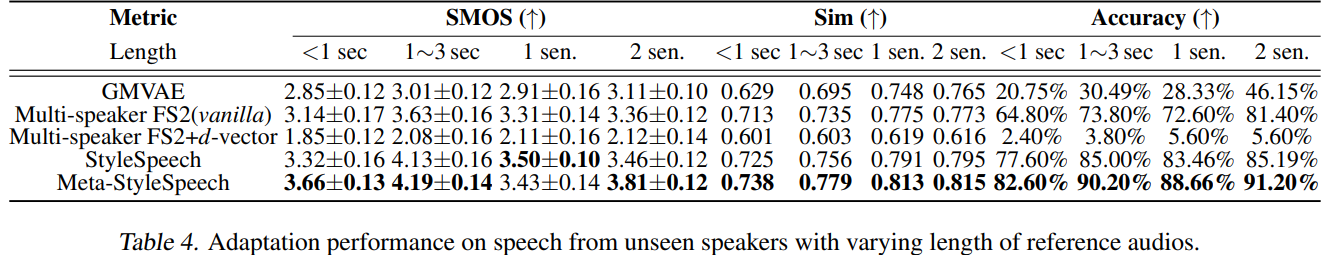
Table 4을 통해 레퍼런스 오디오가 짧아도 StyleSpeech와 Meta-StyleSpeech가 제일 유사도가 높게 합성한다는 것을 알 수 있음.
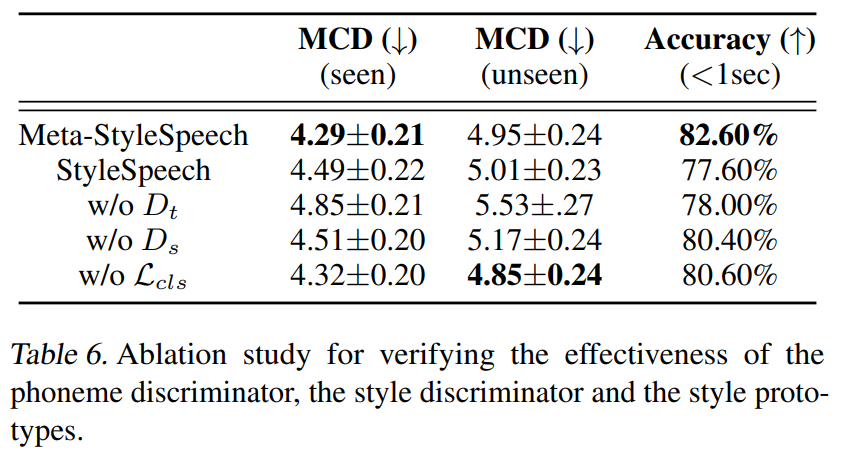
Table 6을 통해 본 모델에서 제안한 아키텍쳐들이 Adpatation 성능을 높이는데에 기여한다는 것을 알 수 있음.
Conclusion
- 짧은 타겟 샘플 오디오로부터 Expressive 하면서 높은 품질의 스피치를 만들어 내는 Multi-speaker adaptive TTS 모델인 StyleSpeech를 제안
- Multi-speaker 스피치의 다양한 스타일을 생성해낼 수 있게 하기 위해서 Style-Adaptive Layer normalization (SALN) 을 제안하고 이를 적용
- Unseen 스피커에 대한 Adaptation 능력을 더욱 향상시키기 위해 Meta-learning 방식과 2개의 Discriminator을 추가적으로 적용함으로써 Meta-StyleSpeech 를 제안
- 실험적인 결과로 StyleSpeech와 Meta-StyleSpeech 둘 다 Seen, Unseen 스피커에 대해 높은 품질의 스피치를 만들어낸다는 것을 알 수 있었고, 1초보다 짧은 레퍼런스 오디오에 대해서 Adaptation을 잘한다는 것을 알 수 있었음
- Future work: Latent space를 Disentangle 하면서 Controllable 스피치 합성
References
-